Ultimate Guide to Cloud Deployment Models: Public, Private, Hybrid & Community Explained
“Before diving into the deployment models, it’s important to understand how cloud computing works and why it has become essential in modern IT.”
Introduction: Why Cloud Deployment Models Matter in the Real World
Cloud computing is no longer just a tech buzzword — it has become the foundation of modern digital transformation. From startups to multinational corporations, nearly every organization is leveraging the cloud to drive innovation, enhance performance, and scale effortlessly.
But here’s the key question:
How exactly is the cloud infrastructure delivered to you or your business?
This is where cloud deployment models come into the picture.
A cloud deployment model refers to the specific environment and architecture in which cloud services are delivered. It defines who owns the infrastructure, where it is located, how it’s managed, and who can access it. Just like choosing a place to live — apartment, villa, co-living space — your cloud setup also depends on your unique needs, budget, control level, and security expectations.
📌 Think of it like transportation options:
Public cloud is like taking the bus — cost-effective, but shared.
Private cloud is your own car — more control, but higher maintenance.
Hybrid cloud is like using your car for city rides and trains for long-distance — smart mix of convenience and control.
Community cloud is like a carpool for professionals — shared with people who have similar destinations and needs.
Choosing the wrong deployment model can lead to performance issues, security risks, regulatory failures, or even overspending on infrastructure you don’t need.
On the other hand, selecting the right deployment model helps:
Optimize costs
Enhance data security and control
Meet industry compliance standards
Enable flexible scaling and reliability
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down the four major cloud deployment models — Public, Private, Hybrid, and Community Cloud — using practical examples, benefits, drawbacks, and ideal use cases.
By the end of this post, you’ll clearly understand:
What each deployment model is
When and why to use each one
How to make the right choice based on your goals
So, whether you’re a student exploring cloud fundamentals, a professional architecting solutions, or a business leader planning cloud adoption — this guide is your go-to reference for mastering cloud deployment models.
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, choosing the right cloud deployment model can make or break an organization’s IT strategy. Businesses that fail to evaluate different cloud deployment models risk overspending on infrastructure or compromising data security. Whether you’re a startup scaling fast or an enterprise seeking control and compliance, aligning your goals with the right cloud deployment model is critical.
Understanding the characteristics of public, private, hybrid, and community cloud deployment models empowers decision-makers to build resilient, scalable, and cost-effective cloud architectures. Each model offers distinct advantages in terms of accessibility, customization, and performance. That’s why many IT leaders first assess various cloud deployment models before moving to service layers like IaaS, PaaS, or SaaS.

Introduction: Understanding the Core of Computing Models
In today’s digital era, computing is the backbone of nearly everything — from mobile apps to AI, online banking to cloud services. But behind the scenes, there’s not just one way computing works. In fact, there are multiple computing models, each designed to handle different kinds of problems, environments, and user needs.
Whether you’re streaming a video on Netflix, training an AI model, running a simulation for weather forecasting, or processing millions of e-commerce transactions — you’re relying on a specific computing model that defines how the data is processed, where the computation happens, and how resources are allocated.
💡 Why does it matter?
Choosing the right computing model impacts speed, efficiency, cost, scalability, and even environmental sustainability.
🧠 What Are Computing Models?
A computing model refers to the method or framework through which computation is performed. This includes the hardware structure, networking logic, and software configuration that determines how inputs are processed to produce outputs.
These models help us understand:
Where computation happens (centralized vs. decentralized)
How resources are managed (shared vs. isolated)
What kind of tasks it handles best (real-time, big data, machine learning, etc.)
📌 In This Guide, You’ll Learn:
The core characteristics of each computing model
When and where they’re used in real life
Pros, cons, and best-use cases
We’ll explore 8 powerful types of computing models, including:
Cloud Computing
Edge Computing
Grid Computing
Quantum Computing
Fog Computing
Parallel Computing
Distributed Computing
High-Performance Computing (HPC)
By the end of this post, you’ll understand which model powers your favorite apps and which ones are shaping the future of AI, automation, and big data
Public Cloud – Affordable, Scalable, and Ready for All
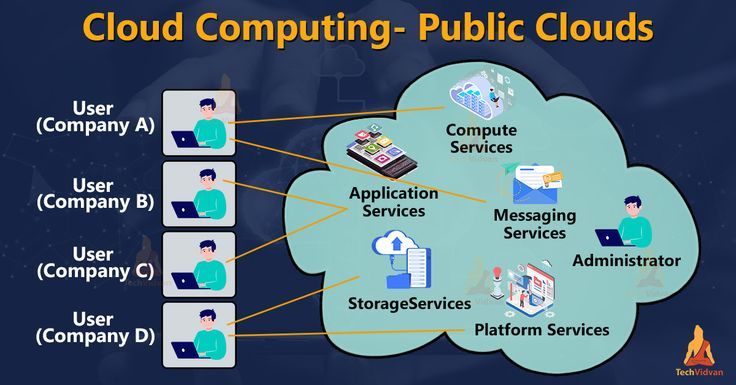
The Public Cloud is the most widely adopted cloud deployment model—and for good reason. It provides on-demand computing services like storage, servers, databases, and networking over the internet, and is managed by third-party providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), IBM Cloud, and others.
These services are made available to the public—anyone can use them, from individual developers to large enterprises—making it a multi-tenant environment where many users share the same infrastructure.
🧠 Understanding the Public Cloud
In the public cloud, all the hardware, software, and supporting infrastructure are owned and managed by the service provider. Users access resources through a web browser or API, paying only for what they consume (known as the pay-as-you-go model).
Unlike traditional infrastructure, there’s no need to buy, install, or maintain servers, which significantly reduces upfront costs and IT burden.
✅ Key Characteristics of Public Cloud
Open Access: Available to anyone over the internet
Shared Resources: Multiple customers use the same infrastructure (multi-tenancy)
Elastic Scalability: Scale resources up or down instantly
Metered Billing: Pay only for what you use
Managed Infrastructure: Provider handles maintenance, updates, and security
💡 Real-Life Examples of Public Cloud Use
A small business hosts its website on AWS EC2 to avoid buying and managing servers.
A developer uses Google Cloud Functions to run code in response to events, like user signups.
A YouTuber stores videos and media assets on Microsoft Azure Blob Storage.
A startup uses Firebase to rapidly build and deploy mobile apps.
Public cloud services are used in web hosting, data analytics, artificial intelligence, application development, e-commerce platforms, and more.
🟢 Advantages of Public Cloud
1. Cost-Effective
You don’t need to purchase expensive infrastructure or hire a full-time IT team. With no upfront capital expense, it’s ideal for startups and SMBs.
2. High Scalability
Public cloud providers offer virtually unlimited scalability. Whether you need to run one server or a thousand, you can scale your resources based on demand instantly.
3. Faster Time to Market
Deploy new applications or services within minutes using pre-configured environments and templates provided by cloud vendors.
4. Global Availability
Public clouds are available across multiple regions and data centers, ensuring high availability and reduced latency for global users.
5. Innovation Friendly
You get access to cutting-edge services like machine learning, big data analytics, containerization, serverless computing, and more.
🔴 Limitations of Public Cloud
1. Security Risks
Because resources are shared among multiple users, there’s a higher risk of data breaches or multi-tenancy vulnerabilities, especially if best practices aren’t followed.
2. Less Control
Organizations may have limited control over the hardware and software stack, which can be a challenge for companies needing custom configurations.
3. Compliance Concerns
Industries like healthcare or finance may have strict data governance laws (e.g., HIPAA, GDPR) that make public cloud usage more complex unless additional compliance layers are implemented.
📊 When to Use Public Cloud?
The public cloud is the best choice when you need:
A cost-effective and quick cloud solution
High elasticity for changing workloads
A platform for development, testing, or deployment
Global accessibility with no infrastructure management
🧑💼 Best Suited For:
Startups and small businesses
Developers and freelancers
E-commerce stores
SaaS product teams
Students and educators
Enterprises offloading non-critical workloads
🚀 Popular Public Cloud Providers
| Provider | Services Highlights |
|---|---|
| AWS | EC2, S3, Lambda, RDS |
| Microsoft Azure | Azure VMs, Blob Storage, Cognitive Services |
| Google Cloud | Compute Engine, BigQuery, Firebase |
| IBM Cloud | Watson AI, Kubernetes Services |
| Oracle Cloud | Autonomous Database, OCI Compute |
🌐 Public Cloud in Action – A Real Case Study
Imagine a fast-growing e-commerce startup preparing for a seasonal sales rush. Instead of buying new physical servers, they spin up virtual machines on AWS to handle the traffic spike. After the sale ends, they scale back to normal usage—paying only for the hours used.
This is agility and cost efficiency at its best.
🧾 Summary
| Feature | Public Cloud |
|---|---|
| Ownership | Third-party provider (e.g., AWS, GCP) |
| Access | Public, internet-based |
| Cost | Low (pay-as-you-go) |
| Scalability | High |
| Security | Moderate (shared responsibility model) |
| Ideal For | Startups, dev teams, global apps |
💬 Pro Tip: Even in public cloud environments, you can boost security by using encryption, VPNs, IAM policies, and deploying apps in isolated virtual networks.
Many businesses use a combination of AWS public and private infrastructure. Learn more from AWS.”
Private Cloud – A Secure and Custom Cloud Deployment Model for Enterprises
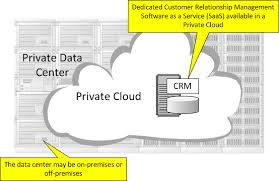
Among all cloud deployment models, the Private Cloud stands out as the most secure and customizable option. It is designed for organizations that demand complete control over their cloud infrastructure, whether for security, compliance, or custom configurations.
Unlike public cloud models, the private cloud deployment model provides a dedicated environment for a single organization. It’s not shared with others, making it ideal for industries like banking, healthcare, defense, and government, where data sensitivity and compliance are top priorities.
🧠 What Is the Private Cloud Deployment Model?
The private cloud is a type of cloud deployment model where all hardware, software, and resources are used exclusively by one organization. It can be hosted:
On-premises (in your own data center)
Or by a third-party provider like IBM Cloud, VMware, or Oracle Cloud
However, access remains restricted—only internal users or systems from that organization can interact with the cloud environment.
This cloud computing model gives full control over security policies, data handling, and infrastructure customization.
✅ Key Features of the Private Cloud Deployment Model
🛡️ Isolated Infrastructure: Single-tenant environment — no sharing with other businesses
🔒 Enhanced Security & Privacy: Sensitive data remains within a controlled boundary
⚙️ Customization: Tailor your cloud to your specific performance and compliance needs
🧾 Regulatory Readiness: Easier to align with laws like HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI-DSS
🖥️ Flexible Hosting: Can be managed in-house or hosted privately by a trusted vendor
💼 Why Organizations Choose the Private Cloud Deployment Model
Many organizations prefer this cloud deployment model because it offers:
Total control over cloud infrastructure
Strict security and data protection
Deep customization of network and compute environments
Greater confidence in meeting industry regulations
This makes the private cloud model essential for:
Financial institutions
Government agencies
Hospitals and research centers
Large enterprises with mission-critical workloads
🟢 Advantages of Private Cloud (Compared to Other Cloud Deployment Models)
✅ Full Control
You manage the environment according to your own policies, configurations, and compliance needs.✅ Strong Security Posture
Since you’re not sharing resources, the risk of external attacks or data leaks is significantly lower.✅ Custom Compliance Setup
This cloud computing model makes it easier to enforce internal security policies and audit trails.✅ High Performance
With dedicated hardware, your workloads are not affected by others’ traffic, ensuring predictable performance.✅ Seamless Integration with Legacy Systems
Private cloud environments can often be integrated with on-premises systems, helping companies modernize gradually.
🔴 Challenges of the Private Cloud Deployment Model
Despite its strengths, this cloud deployment model also comes with limitations:
💰 High Cost
Setting up and managing your own private cloud infrastructure requires a significant upfront investment.🔧 Maintenance Responsibilities
You (or your provider) must handle system updates, backups, and security patching.🧱 Scalability Constraints
Scaling up often requires physical expansion, unlike public cloud where resources are instantly available.
📊 Use Cases – When to Choose the Private Cloud Deployment Model
You should adopt a private cloud model when:
You’re in a highly regulated industry
Your organization deals with sensitive personal or financial data
You require complete customization of infrastructure
You need reliable, isolated performance for critical apps
🏢 Popular Providers of Private Cloud Services
| Provider | Specialty in Private Cloud |
|---|---|
| IBM Cloud | AI-powered private cloud solutions |
| VMware Cloud | Enterprise-ready virtualization & cloud management |
| Oracle Cloud | Private database cloud deployments |
| HPE GreenLake | On-prem private cloud as a service |
| Dell APEX | Flexible private cloud infrastructure |
📚 Real-World Scenario: Private Cloud in Action
A healthcare organization needs to store and process patient health records while complying with HIPAA regulations. By choosing a private cloud deployment model, they host all applications and data on dedicated infrastructure within their internal network or via a secure third-party provider. This ensures:
Data is not exposed to other users
Compliance audits are easier
Internal IT teams retain full control
🧾 Private Cloud Model Summary
| Feature | Private Cloud |
|---|---|
| Type | Cloud Deployment Model |
| Ownership | Single organization |
| Access | Internal/Restricted |
| Security | Very High |
| Scalability | Medium (depends on infrastructure) |
| Cost | High (CapEx + OpEx) |
| Best For | Large enterprises, regulated industries |
🔐 Pro Tip: If you want private cloud benefits but need cloud agility too, consider a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) — a private environment within a public cloud platform like AWS or Azure.
Hybrid Cloud – The Flexible and Balanced Cloud Deployment Model
The Hybrid Cloud deployment model is a powerful combination of private and public cloud infrastructures, enabling businesses to enjoy the best of both worlds. It allows applications and data to move seamlessly between private and public environments, offering flexibility, scalability, and control.
In the landscape of modern cloud deployment models, the hybrid cloud model is widely adopted by organizations that want to keep sensitive data secure in a private cloud while leveraging public cloud scalability for less critical tasks.
🧠 What Is Hybrid Cloud?
Hybrid Cloud is a cloud computing model where an organization uses both public and private clouds and integrates them through a secure network or orchestration tools.
For example, a company can:
Store customer data in a private cloud for security.
Run its website and app infrastructure on a public cloud like AWS or Azure.
Connect both environments to work as a single, unified system.
This approach is ideal for companies that need to balance performance, cost-efficiency, and security.
✅ Key Features of the Hybrid Cloud Deployment Model
🔁 Combines Private & Public Clouds
🔐 Sensitive data stays in private cloud
☁️ Scalable services run on public cloud
🔄 Interconnected through orchestration tools (like Kubernetes, OpenShift)
💡 Smart workload distribution based on needs
🟢 Benefits of Hybrid Cloud
✅ Flexibility & Optimization
Organizations can place each workload in the most suitable environment — secure, low-latency processing in private cloud, and high-volume scalability in public cloud.✅ Cost-Efficiency
Instead of building everything in-house, you can use public cloud resources only when needed, reducing capital expenditure.✅ Improved Business Continuity
If the private cloud goes down, workloads can automatically shift to public cloud — ensuring high availability and disaster recovery.✅ Gradual Cloud Migration
Companies can move to the cloud in phases without abandoning their existing on-premises infrastructure.
🔴 Challenges of Hybrid Cloud
Complex Integration: Connecting public and private clouds securely can be technically challenging.
Security Consistency: Ensuring uniform security policies across both environments is essential.
Cost Tracking: If not managed well, combining two environments may increase operating complexity and cost.
📚 Real-Life Example: Hybrid Cloud in Action
A retail enterprise stores its customer data and payment processing system in a private cloud for security, but uses public cloud services during seasonal sales to handle high website traffic and inventory processing.
This smart use of the hybrid cloud deployment model ensures data privacy, high performance, and cost savings.
🧾 Hybrid Cloud Model Summary
| Feature | Hybrid Cloud |
|---|---|
| Type | Cloud Deployment Model |
| Ownership | Mixed (Private + Public) |
| Access | Controlled (based on environment) |
| Security | High (requires policy alignment) |
| Scalability | Very High |
| Cost | Moderate to High |
| Best For | Enterprises needing flexibility |
💡 Pro Tip: Use hybrid cloud with edge computing for real-time data processing close to users while central systems stay secured in private cloud.
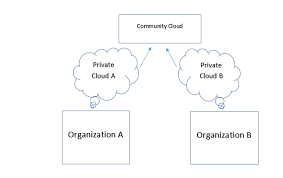
Community Cloud – A Collaborative Cloud Deployment Model for Shared Goals
The Community Cloud deployment model is designed for a group of organizations with similar requirements and shared concerns, such as security, compliance, or performance.
In this model, the cloud infrastructure is shared among multiple organizations (called a community) but is managed either internally or by a third-party vendor. All members benefit from cost savings, joint control, and tailored solutions specific to their field.
🧠 What Is a Community Cloud?
The community cloud model is a multi-tenant cloud deployment model where organizations with common goals—such as government bodies, healthcare institutions, or financial firms—share a dedicated cloud environment.
It offers the collaboration of public cloud and security of private cloud, allowing community members to work efficiently while maintaining compliance and privacy.
✅ Key Features of the Community Cloud Deployment Model
👥 Shared Infrastructure among similar organizations
🔐 Common Security and Privacy Requirements
🤝 Collaborative Control and Management
🧾 Compliance-Oriented Design
🏢 Tailored for Industry Needs (e.g., education, finance, research)
🟢 Benefits of Community Cloud
✅ Cost Sharing
Instead of each organization building their own private cloud, they share resources and split the costs, reducing individual IT burden.✅ Standardized Security
All members adhere to a mutually agreed security and compliance framework, making it easier to maintain data integrity.✅ Collaborative Innovation
Organizations can share tools, data, and research, leading to faster innovation and more efficient operations.✅ Regulatory Compliance
Perfect for sectors that require common compliance standards like FERPA (education), HIPAA (healthcare), or FINRA (finance).
🔴 Challenges of Community Cloud
Governance Complexity: Shared ownership requires clear rules and communication among all members.
Limited Customization: Individual users may have less flexibility compared to a private cloud.
Scaling Decisions Are Shared: All members must agree on changes to scale or upgrade systems.
📚 Real-Life Example: Community Cloud in Action
A group of public universities create a community cloud to store research data, learning management systems (LMS), and digital libraries. They share costs and ensure the environment is secure, compliant with educational regulations, and tailored to academic workflows.
🧾 Community Cloud Model Summary
| Feature | Community Cloud |
|---|---|
| Type | Cloud Deployment Model |
| Ownership | Multiple organizations (shared) |
| Access | Restricted to community members |
| Security | High (industry-aligned) |
| Scalability | Medium |
| Cost | Shared |
| Best For | Universities, government alliances, NGOs |
🤝 Pro Tip: Use community clouds for joint government projects, cross-university platforms, or multi-hospital medical research, where data sharing with security is essential.
How Cloud Deployment Models Affect Business Growth
Choosing the right cloud deployment model isn’t just a technical decision—it’s a strategic move that directly impacts your business’s flexibility, cost-efficiency, and scalability. As organizations adopt digital transformation initiatives, understanding how different cloud deployment models influence infrastructure and operational workflows becomes increasingly important.
Public clouds allow companies to scale quickly without heavy capital investments. This can accelerate time-to-market and enable startups or small businesses to compete on a global scale. In contrast, private cloud deployment models support strict compliance needs, which is vital for industries like healthcare, finance, and government.
Hybrid cloud deployment models empower businesses to maintain control over critical workloads while leveraging public cloud resources for less-sensitive operations. This dual approach is increasingly favored by companies that need both speed and control. Community cloud deployment models, meanwhile, foster collaboration between institutions with shared goals—common in education and research.
The key takeaway? Your choice of cloud deployment model can directly support your company’s mission, reduce risk, and maximize return on cloud investments.
When to Choose the Right Cloud Deployment Model
Choosing the right cloud deployment model is a strategic decision that depends heavily on your organization’s structure, data sensitivity, and growth plans.
If you’re a startup or a growing business looking to launch quickly without investing heavily in IT infrastructure, the public cloud is your best bet. It offers the agility, scalability, and low upfront costs that are perfect for rapid innovation and scaling on demand.
For organizations that deal with highly sensitive data—such as banks, government bodies, or healthcare institutions—the private cloud is ideal. It provides complete control over your cloud environment, ensuring strict security, compliance, and data governance.
When your business needs both security and flexibility, the hybrid cloud stands out. It allows you to keep your critical data in a private cloud while taking advantage of the public cloud’s scalability for general operations or traffic spikes.
If your organization is part of a group with shared objectives—such as universities collaborating on research or government agencies working on a joint initiative—the community cloud offers a tailored solution. It enables secure collaboration with aligned compliance standards and shared infrastructure.
Real-World Use Cases
🔐 Private Cloud – Banking Sector
A multinational bank uses a private cloud to manage customer transactions, ensuring all operations stay compliant with financial regulations and remain secure from breaches.
🌍 Public Cloud – E-commerce Startup
An online retail startup hosts its web app on AWS, using public cloud infrastructure to scale during flash sales while keeping costs low.
🔄 Hybrid Cloud – Healthcare Provider
A hospital stores patient records in a private cloud (to comply with HIPAA) and runs appointment apps on the public cloud for easier scalability.
🤝 Community Cloud – Educational Institutions
Several universities pool resources to create a secure community cloud for storing shared research, digital libraries, and collaborative academic tools.
Selecting the best fit from the available cloud deployment models depends on a range of factors like workload type, compliance needs, and budget. For example, if your business handles sensitive data, a private cloud may be more suitable. On the other hand, organizations looking for rapid scalability and cost efficiency often go with public cloud deployment models.
Hybrid and community cloud deployment models are gaining popularity as they blend flexibility and security, enabling organizations to optimize their infrastructure while maintaining compliance. The key is to evaluate your business objectives against the features offered by each cloud deployment model and choose the one that aligns with both current and future needs.
Future of Cloud Deployment Models
The future of cloud deployment models lies in even more flexibility, automation, and intelligent workload placement. As businesses adopt artificial intelligence, machine learning, and edge computing, deployment models will evolve to meet new performance demands and compliance standards.
Hybrid and multi-cloud deployments will dominate as organizations aim to avoid vendor lock-in and optimize costs. Tools like container orchestration (e.g., Kubernetes) and Infrastructure as Code (IaC) are making it easier to switch or blend cloud deployment models based on workload type.
Staying updated on the latest cloud deployment trends ensures your business remains agile, competitive, and future-ready.
Final Thoughts: Choosing the Right Cloud Deployment Model
In the ever-evolving world of cloud computing, selecting the right cloud deployment model is a strategic decision that shapes your security, performance, and long-term scalability.
Each model—Public, Private, Hybrid, and Community Cloud—offers its own blend of benefits. Whether you’re a startup launching a new app, a hospital securing patient data, or a university collaborating on research, there’s a cloud model built for you.
The right cloud deployment model isn’t just about technology—it’s about your business vision, compliance needs, and growth strategy.
💬 Need help deciding? Drop a comment below or explore more posts on CreativeDataAI to keep learning.
🔗 Keep exploring the cloud.