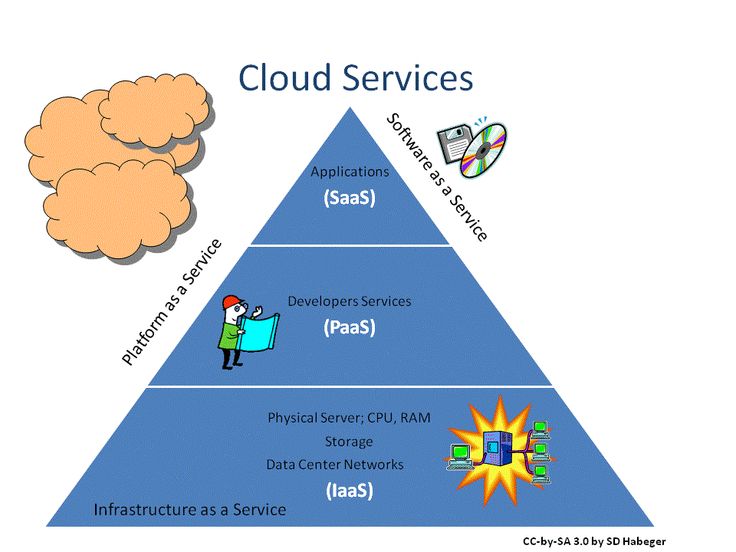
Cloud Computing Models Explained: IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS Made Simple
Introduction: What Are Cloud Computing Models?
In the digital age, we use cloud services every day — from checking email and storing photos to building apps and managing servers. But have you ever wondered how these services are delivered?
That’s where cloud computing models come in.
Cloud computing models define how cloud services are offered to users. They categorize cloud services based on the level of control, customization, and management required by the user.
There are three primary cloud computing models:
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
PaaS (Platform as a Service)
SaaS (Software as a Service)
Each model offers a different level of abstraction, flexibility, and ease of use.
To understand the foundation, check out our guide on How Cloud Computing Works.
Deep Dive into IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is the foundational layer of cloud computing models. It provides on-demand access to essential computing resources — such as virtual machines (VMs), storage, and networking — all delivered over the internet.
Think of IaaS as renting the core building blocks of IT infrastructure without owning any physical hardware.
1. What Is IaaS?
IaaS is a cloud computing model where cloud providers deliver and manage physical data center resources virtually. Instead of buying servers or maintaining on-site hardware, users can rent computing resources from providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud.
You manage:
The operating system
Applications
Data
Middleware
The provider manages:
The physical servers
Storage
Networking
Data center infrastructure
2. Why Use IaaS?
IaaS offers maximum flexibility and control, making it perfect for businesses that want to manage everything themselves — except the physical hardware.
Key Benefits:
Full Customization – Install your own OS, frameworks, and tools.
Scalability – Easily scale resources up or down based on demand.
Cost Efficiency – Pay only for the resources you use.
Integration – Works well with DevOps tools, APIs, and automation scripts.
Example: A startup wants to host a web app and manage the server themselves. Instead of buying hardware, they launch a virtual server on AWS EC2, install Linux, set up Apache, and deploy their app — all in hours, not days.
3. Common Use Cases of IaaS
Web Hosting
Create and manage servers for websites, portals, or eCommerce stores.
Dev/Test Environments
Quickly spin up and destroy virtual environments for software development and testing.
Big Data Analytics
Use IaaS to process large volumes of data without investing in expensive infrastructure.
Backup and Disaster Recovery
Store backups and replicate servers in the cloud for safety and compliance.
High-Performance Computing (HPC)
Run simulations, financial modeling, or machine learning on powerful virtual infrastructure.
4. Real-World Analogy: IaaS is Like Renting Land
Imagine you want to build a custom house. You rent an empty plot of land (IaaS), and then you decide:
What to build
What tools to use
How to maintain it
You have full control — but you’re also responsible for everything built on top.
That’s exactly how IaaS works in the cloud.
5. Popular IaaS Providers
| Provider | Key Service | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Amazon Web Services | EC2, S3, VPC | Scalable VMs, storage, global availability |
| Microsoft Azure | Azure VMs | Windows/Linux VM support, hybrid cloud tools |
| Google Cloud | Compute Engine | Fast performance, live migration of VMs |
| IBM Cloud | Virtual Servers | Enterprise-grade performance and security |
| Oracle Cloud | OCI Compute | Optimized for databases and enterprise workloads |
6. Security in IaaS
In IaaS, you are responsible for securing:
The operating system
Firewalls and access control
Applications and data
The provider secures:
The infrastructure
Physical hardware
Network and virtualization layers
Tip: Always use firewalls, encryption, and secure access policies when using IaaS platforms.
7. Challenges of IaaS
While IaaS is powerful, it comes with its own learning curve:
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Complex Setup | Requires knowledge of OS, security, and server setup |
| Ongoing Maintenance | You must handle patching, updates, and backups |
| Billing Complexity | Costs can rise if not monitored carefully |
| Vendor Lock-in | Migrating between providers can be technically difficult |
It’s ideal for teams with technical knowledge or those working with DevOps pipelines.
8. Summary: Why IaaS Is a Powerful Cloud Computing Model
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Flexibility | Build and configure your infrastructure your way |
| Cost-Effective | Pay only for what you use — no upfront hardware costs |
| Global Reach | Deploy apps across multiple regions easily |
| Integration-Ready | Seamlessly connect with APIs, tools, databases |
| Ideal For | Developers, system architects, and IT professionals |
Final Thoughts on IaaS
Infrastructure as a Service is a critical part of the cloud computing models stack. It gives users complete control and scalability, without the burden of managing physical hardware. For businesses and tech professionals who want maximum flexibility and performance, IaaS is the go-to model.
Whether you’re deploying a web app, testing software, or running big data projects — IaaS is the robust, scalable foundation that modern cloud computing is built upon.
Learn more about Amazon EC2 – IaaS from AWS

Deep Dive into PaaS (Platform as a Service)
Platform as a Service (PaaS) is a cloud computing model that provides a ready-made development and deployment environment in the cloud. Developers can build, test, and deploy applications without managing infrastructure like servers, networks, or storage.
In short, PaaS lets you focus on coding while the platform takes care of the rest.
1. What Is PaaS?
PaaS provides a platform — including the operating system, development tools, databases, and web servers — so developers can create applications quickly and efficiently. You write the code, and the provider manages everything underneath.
You manage:
Application code
Data
App configuration
The provider manages:
Infrastructure (servers, storage)
Operating system
Middleware
Runtime environment
2. Why Use PaaS?
PaaS is all about speed, productivity, and automation. It helps teams avoid the repetitive, time-consuming tasks of managing hardware and software dependencies.
Key Benefits:
Rapid Development – Launch apps in days instead of weeks.
Built-In Tools – Frameworks, SDKs, APIs, CI/CD pipelines.
Automatic Scaling & Updates – No need to configure servers.
Cost-Effective – Pay for the platform, not the infrastructure.
Example: A team wants to build a mobile app. They choose Google App Engine, upload their code, and the platform automatically manages hosting, scaling, and updates — so they can focus on app features.
3. Common Use Cases of PaaS
Application Development
Quickly create web or mobile applications using pre-configured environments.
Microservices Deployment
Host multiple independent services using APIs and containers.
Continuous Integration/Delivery (CI/CD)
Automate testing and deployment pipelines.
API Management
Create and expose APIs securely, with rate limiting and analytics.
4. Real-World Analogy: PaaS is Like a Managed Kitchen
Imagine you walk into a fully-equipped kitchen where all appliances, ingredients, and tools are ready. You just cook your dish and serve it.
That’s PaaS — the platform handles the infrastructure, and you focus on development.
5. Popular PaaS Providers
| Provider | Key PaaS Service | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Google Cloud | App Engine | Fully managed, auto-scaling web app platform |
| Microsoft Azure | Azure App Service | Supports .NET, Node.js, PHP, Python, and more |
| Heroku | Heroku Platform | Easy deployment with Git, built-in add-ons |
| Red Hat OpenShift | OpenShift | Container-based PaaS for enterprise applications |
| Engine Yard | Engine Yard Platform | Ruby on Rails and PHP support |
6. Security in PaaS
PaaS platforms offer built-in security and updates, but you’re still responsible for:
Securing your application code
Managing authentication and authorization
Input validation and data protection
The provider handles:
OS patches and runtime updates
Server and infrastructure security
Monitoring and logs
Tip: Always use strong access controls and encryption for your app data.
7. Challenges of PaaS
While PaaS simplifies development, it also introduces some limitations:
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Vendor Lock-In | Apps may depend heavily on a provider’s ecosystem |
| Limited Customization | You can’t modify OS or middleware settings |
| Performance Issues | Shared platforms may affect performance in peak times |
| Pricing Complexity | Can be costly if not monitored (especially add-ons, APIs) |
Ideal for teams that value development speed over deep infrastructure control.
8. Summary: Why PaaS Is a Key Cloud Computing Model
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Developer-Focused | Write code and deploy without worrying about infrastructure |
| Rapid Time to Market | Ideal for agile teams and MVPs |
| Built-In Tools | Pre-installed libraries, runtimes, and dev frameworks |
| Ideal For | App developers, startups, and DevOps teams |
Final Thoughts on PaaS
Platform as a Service (PaaS) is a crucial part of modern cloud computing models. It empowers developers to build scalable, secure applications faster by abstracting away the infrastructure layer.
Whether you’re creating a web app, deploying a microservice, or running a CI/CD pipeline — PaaS simplifies the process and gets your ideas into production faster.
It’s the perfect balance between control and convenience.
Official docs: Google App Engine – PaaS from Google Cloud

Deep Dive into SaaS (Software as a Service)
Software as a Service (SaaS) is the most user-friendly cloud computing model. It delivers fully functional software applications over the internet — without users needing to install, manage, or maintain anything.
With SaaS, you just open your browser, log in, and start using the app.
1. What Is SaaS?
SaaS provides ready-to-use software hosted in the cloud. It’s accessed via a web browser or app and is managed entirely by the cloud provider.
You don’t worry about:
Installation
Updates
Hardware
Security patches
You manage:
Only your data and usage preferences.
The provider manages:
Everything — including servers, databases, updates, security, and software versions.
2. Why Use SaaS?
SaaS eliminates complexity and upfront costs, making it ideal for individuals, teams, and businesses who want fast access to powerful tools without technical overhead.
Key Benefits:
No Setup Required – Start using the service instantly.
Automatic Updates – Always using the latest version.
Access from Anywhere – Use it on any device, anytime.
Subscription Pricing – Pay monthly or yearly per user.
Example: You use Gmail to send emails or Google Docs to create files. You didn’t install anything, you didn’t manage servers — and it just works. That’s SaaS in action.
3. Common Use Cases of SaaS
Email & Productivity
Send emails, manage calendars, and create documents (e.g., Gmail, Outlook, Google Docs).
Team Collaboration
Manage projects, chat, and share files (e.g., Slack, Trello, Notion).
CRM and Marketing
Handle customer data, automate sales and email campaigns (e.g., Salesforce, Mailchimp).
eCommerce and Accounting
Run online stores or manage finances (e.g., Shopify, QuickBooks Online).
4. Real-World Analogy: SaaS is Like Netflix
Imagine using Netflix — you don’t install DVDs or worry about the video format. You just sign in and stream.
SaaS is the same — software is delivered over the cloud, ready to use, with zero technical setup.
5. Popular SaaS Providers
| Provider | Key SaaS Product | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Google Workspace | Docs, Sheets, Drive, Gmail — all cloud-native | |
| Microsoft | Office 365 | Word, Excel, Outlook online |
| Zoom | Zoom Video Conferencing | Cloud-based meetings and webinars |
| Dropbox | Cloud Storage | File sharing and backup |
| Salesforce | CRM Platform | Manage leads, customers, and sales workflows |
| Trello | Project Management | Task tracking and collaboration tools |
6. Security in SaaS
In SaaS, the provider handles all the security, uptime, and compliance — but as a user, you’re still responsible for:
Setting strong passwords and enabling 2FA
Managing who has access to your account
Protecting sensitive data you upload
Tip: Choose SaaS tools with SSL encryption, GDPR compliance, and role-based access features for maximum data safety.
7. Challenges of SaaS
While SaaS is easy to use, there are a few limitations and concerns:
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Limited Customization | You can’t change how the software works internally |
| Data Ownership | Your data is stored on third-party servers |
| Vendor Lock-in | Migrating to a different SaaS provider can be difficult |
| Internet Dependency | Requires a reliable internet connection |
Best suited for users and teams who want functionality over flexibility.
8. Summary: Why SaaS Is the Most Popular Cloud Computing Model
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Ready-to-Use | Just sign in and start using the software |
| Zero Maintenance | Provider handles updates, bugs, and downtime |
| Accessible Anywhere | Use on web, mobile, or tablet with internet |
| Ideal For | Individuals, small businesses, non-tech users |
Final Thoughts on SaaS
Software as a Service (SaaS) has redefined how we work, communicate, and manage daily tasks. As the most accessible layer of the cloud computing models, SaaS allows users to focus on outcomes — not on installation, updates, or security.
Whether you’re sending emails, managing customers, or running a business, SaaS helps you do it all — instantly, from the cloud.
From Gmail to Zoom, Trello to Shopify, the world’s favorite tools run on SaaS — and so can your next idea.

Real-Life Analogy
Think of cloud computing models like transportation:
IaaS = Renting a car — you drive, maintain, and control everything.
PaaS = Taking a taxi — you choose the destination; the driver handles the ride.
SaaS = Taking the metro — everything is set up for you, just hop in and go!
Want a more technical breakdown? Check out this detailed guide by IBM on IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS to explore more use cases and diagrams.
Why Cloud Computing Models Matter
Understanding cloud computing models is essential for businesses and learners alike because they define how cloud services are structured and accessed. Each model—public, private, hybrid, or community—offers distinct advantages depending on your needs. By choosing the right cloud computing model, organizations can optimize security, performance, and cost.
For beginners or professionals planning infrastructure, a strong grasp of different cloud computing models ensures that you’re designing solutions that scale, comply with regulations, and meet technical goals efficiently.
Various industries adopt different cloud computing models based on their specific needs:
Public cloud models are popular among startups for their scalability and cost-efficiency.
Private cloud models are used in healthcare and finance sectors where data privacy is critical.
Hybrid cloud computing models allow businesses to maintain sensitive data in-house while using public cloud for less sensitive tasks.
Community cloud models are favored by universities and government agencies that share infrastructure for a common goal.
These examples show how cloud computing models are applied in the real world to solve practical problems.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Cloud Computing Model
In today’s fast-moving digital world, cloud computing models are more than just tech buzzwords — they are the foundation of how modern software and services are built, delivered, and scaled. Whether you’re a developer, entrepreneur, student, or business leader, understanding these models is key to making smarter, future-ready decisions.
Let’s recap:
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) gives you complete control over infrastructure. It’s perfect for tech-savvy teams who need flexibility and want to build their own custom environments.
PaaS (Platform as a Service) simplifies development by handling the backend. It’s ideal for developers who want to focus only on coding and launching apps quickly.
SaaS (Software as a Service) delivers ready-to-use tools over the internet. It’s best for individuals or teams who just want to “use the app” without managing anything technical.
Each model plays a unique role in the cloud computing ecosystem. The right choice depends on your goals, team skills, scalability needs, and budget.
Pro Tip: You don’t have to choose just one model. Many businesses today use a combination of all three — for example, running their backend on IaaS, building apps with PaaS, and using SaaS tools like Gmail, Zoom, or Slack.
Final Thoughts
By understanding how these cloud computing models work, you’re better prepared to:
Launch faster
Save money
Scale smartly
Adapt to the future of technology
Whether you’re starting a small project or running a large enterprise, cloud computing models give you the tools to build smarter and grow faster — without the need to invest in physical infrastructure or complex IT systems.
By understanding the differences between these cloud computing models, you’re better equipped to make smart decisions about deploying apps, managing data, or running services. Whether you’re launching a tech startup or moving legacy systems to the cloud, knowing how these models work is essential.
Keep Exploring!
If you found this guide helpful, don’t stop here:
🔗 Explore: IaaS vs. PaaS vs. SaaS – IBM Cloud
- By exploring these resources, you’ll gain a broader understanding of not only the cloud computing models themselves but also how they integrate into the future of digital infrastructure, AI, and data-driven services.
Let’s Connect!
Have questions? Need help choosing the right model for your project?
Drop a comment below — I’d love to help!